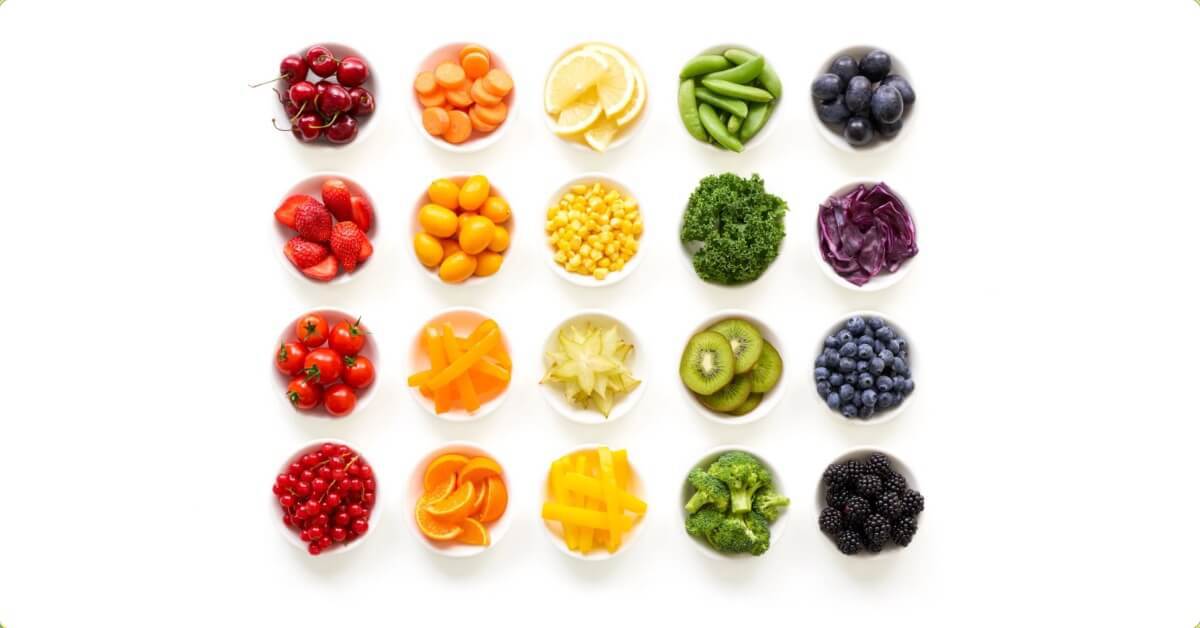
The Color of Fruits and Vegetables: What Are They and What Do They Affect?
There are five different color categories of fruits and vegetables, each with its own unique set of phytochemicals. Fruits and vegetables are divided into five different color categories: red vegetables, purple/blue vegetables, orange vegetables, green vegetables, and white and brown vegetables. Each color of fruits and vegetables carries its own unique set of disease-fighting chemicals called phytochemicals. These phytochemicals give fruits and vegetables their vibrant colors and, of course, some of their health benefits. Eating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables can ensure you get a diverse range of nutrients.
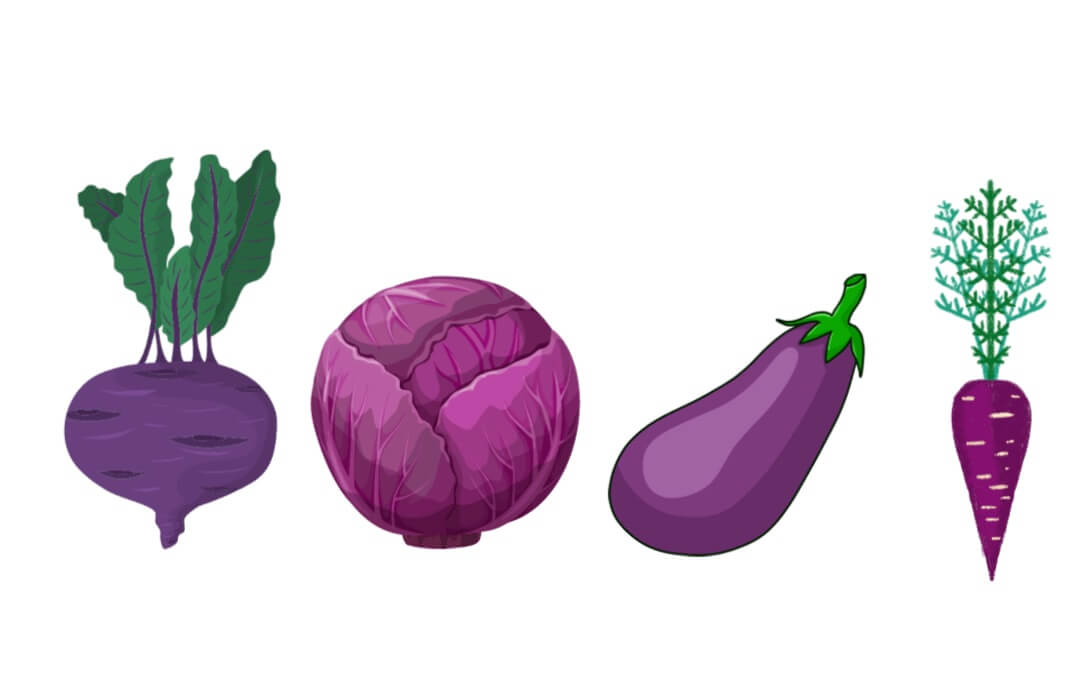
Purple and Blue Vegetables
Purple and blue rainbow foods contain the same types of plant nutrients that also give them their unique color. The plant pigment anthocyanin gives blue/purple fruits and vegetables their characteristic color. Anthocyanin also has antioxidant properties that protect cells from damage and may help reduce the risk of cancer, stroke, and heart disease.
| Eggplant | Beet | Purple Bell Pepper |
| Purple Cabbage | Purple Carrot | Purple Cauliflower |
| Purple Potato | Turnip | Blackberry |
| Blueberry | Fig | Plum |
| Purple Grape | Raisin | Prunes |
Red Vegetables
Red fruits and vegetables are colored by a natural plant pigment called lycopene. Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that may help reduce the risk of cancer and maintain heart health. Red foods in the rainbow diet are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory molecules that prevent inflammation and oxidative stress.
| Red Cabbage | Red Potato | Red Bell Pepper |
| Tomato | Beet | Red Onion |
| Red Chicory (Radicchio) | Red Chard | Red Jalapeño Pepper |
| Apple | Blood Orange | Cherry |
| Cranberry | Lingonberry | Nectarine |
| Pink Grapefruit | Pomegranate | Raspberry |
| Red Currant | Red Pear | Red Plum |
| Strawberry | Watermelon |
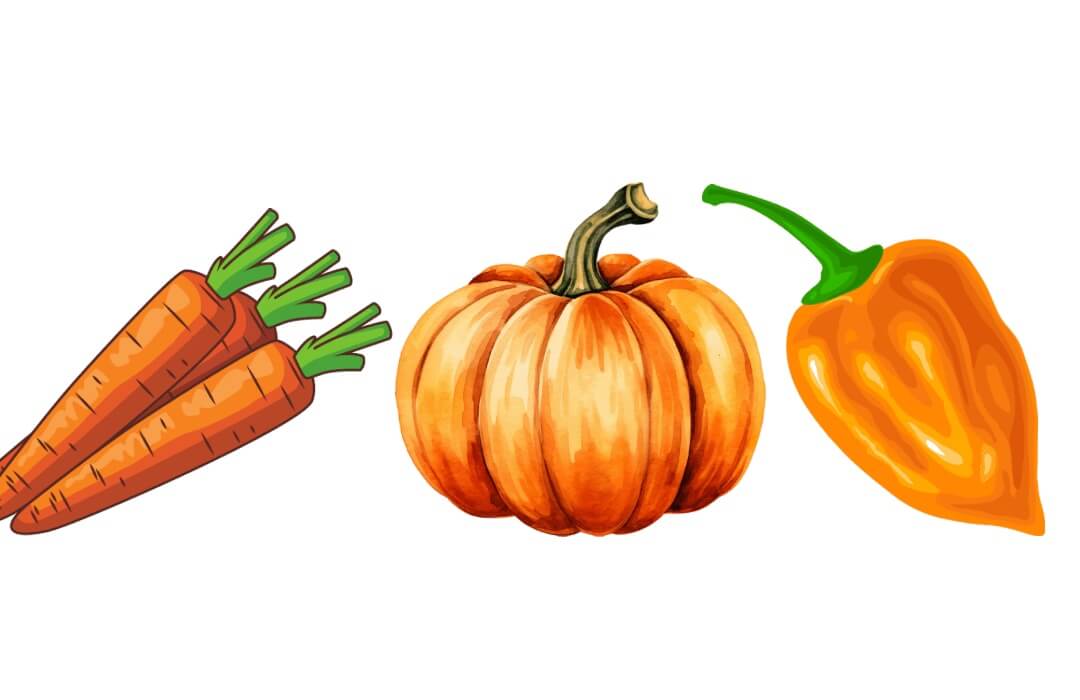
Orange Vegetables
Orange foods contain phytonutrients similar to red rainbow foods, such as beta-carotene, which gives fruits and vegetables a rich orange-red hue. It converts into vitamin A, which helps maintain the health of mucous membranes and eyes. The benefits of orange fruits and vegetables also support the reproductive health of men and women.
| Carrot | Orange Bell Pepper | Pumpkin |
| Turmeric | Sweet Potato | Yam |
| Apricot | Persimmon | Cantaloupe |
| Kumquat | Tangerine | Mango |
| Nectarine | Orange | Papaya |
| Passion Fruit | Peach | Persimmon |
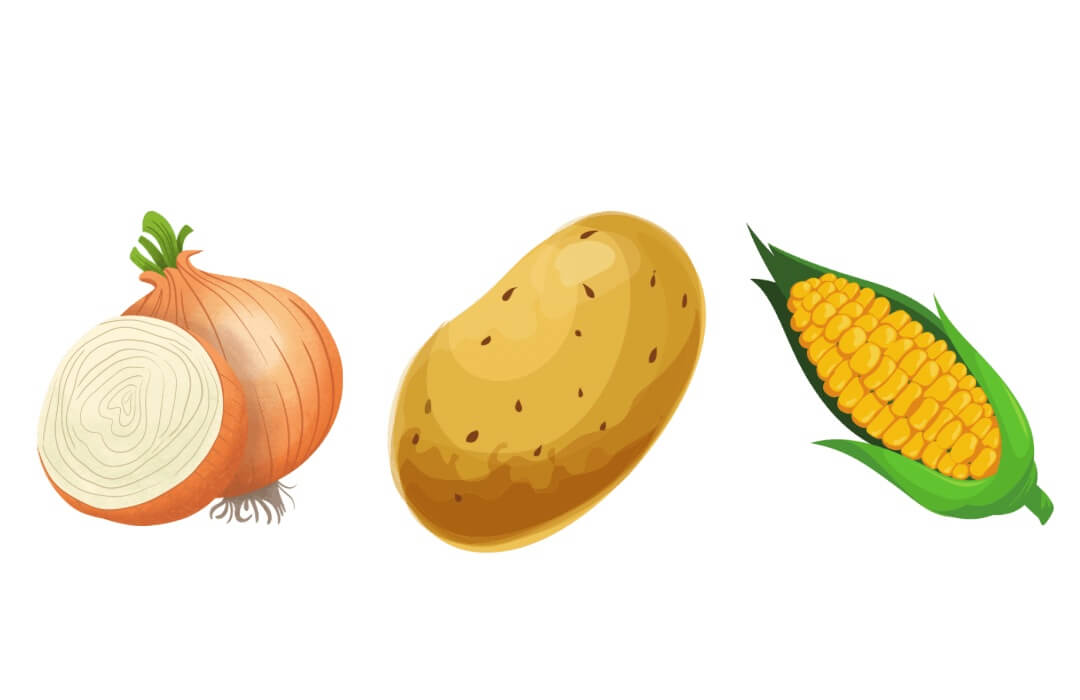
Yellow Vegetables
Yellow foods are particularly beneficial for your digestive tract. They contain prebiotics that stimulate your gut bacteria to produce short-chain fatty acids—special molecules that nourish the cells of your gut.
| Corn | Ginger | Yukon Potato |
| Yellow Bell Pepper | Yellow Onion | Banana |
| Apple | Asian Pear | Lemon |
| Pineapple |
Green Vegetables
Green foods in the rainbow diet contain nutrients that are particularly good at protecting your cardiovascular system from oxidative stress. Specifically, oxidative stress is associated with high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries), and heart disease.
| Artichoke | Avocado | Bean Sprouts |
| Sweet Bell Pepper | Broccoli | Cabbage |
| Celery | Edamame | Green Beans |
| Green Peas | Beet Greens | Kale |
| Green Chard | Mustard Greens | Spinach |
| Okra | Watercress | Green Tea |
| Green Apple | Kiwi | Lime |
| Olives | Pears |
White and Brown Vegetables
White fruits and vegetables contain a range of health-promoting phytochemicals, such as allicin (found in garlic), which is known for its antiviral and antibacterial properties. Some representatives of the white group, such as bananas (green) and potatoes, are also good sources of potassium.
| Onion | Garlic | Radish |
| Cauliflower | Pattypan Squash | Celeriac (Celery Root) |
For maximum health benefits, include seasonal vegetables and berries of different colors in your diet every day.











0 Comments